In the realm of consumer hardware, the dominance of x86 and ARM architectures has long overshadowed other contenders. However, Milk-V is now shaking up the landscape with its latest offering, the Jupiter mini-ITX motherboard, heralding a substantial leap for RISC-V architecture. The Jupiter motherboard signifies not only technological innovation but also a strategic move to capture the burgeoning Chinese market. Designed to offer competitive specifications within a compact form factor, this new product aims to reshape perceptions and applications of RISC-V technology, which for long has been more of an academic curiosity than a commercial contender.
RISC-V is an open-source hardware instruction set architecture (ISA) that has long been celebrated for its potential to democratize access to cutting-edge computing technology. Historically, the adoption of RISC-V has been limited to niche applications and academic experiments. Yet, recent trends driven by geopolitical factors and technological sovereignty interests, particularly in China, have spurred renewed interest and investment in RISC-V. The debut of Milk-V’s Jupiter motherboard marks a noteworthy milestone in bringing RISC-V closer to mainstream consumer applications. Unlike proprietary architectures like x86 and ARM, RISC-V offers greater customization and potentially lower costs, thanks to its open-source nature. Milk-V aims to leverage these advantages to cater to the unique demands of the Chinese market, where the appetite for indigenous technology solutions is rapidly growing. Therefore, the Jupiter motherboard is not merely a new product but also a symbol of a broader shift toward embracing open-source hardware solutions.
Technical Specifications and Features
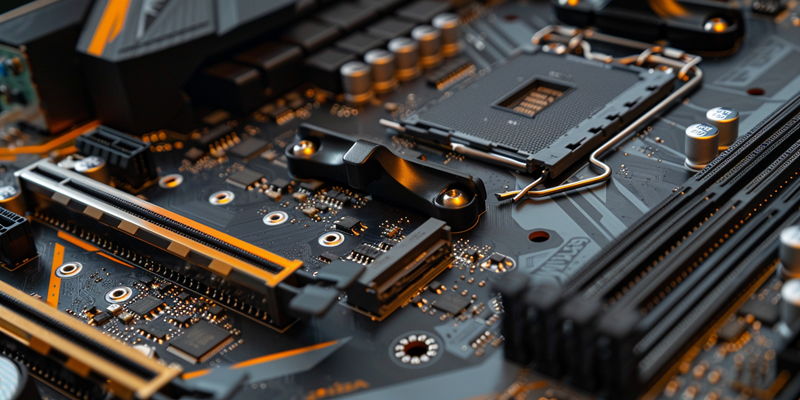
Delving into the technical aspects, the Jupiter motherboard distinguishes itself with its compact mini-ITX form factor, measuring 170mm x 170mm. This versatile design makes it suitable for a variety of setups, ranging from home-built PCs to specialized embedded systems. The heart of Jupiter is its SpacemiT K1 RISC-V processor, which features eight cores and delivers 2 TOPS (Tera Operations Per Second) of AI power. This robust processor showcases the capability of RISC-V architecture to handle complex computing tasks and modern AI workloads efficiently. The motherboard supports multiple memory options, including configurations of 4GB, 8GB, or 16GB of LPDDR4x RAM, thus providing flexibility to meet a range of user requirements from basic applications to more demanding computational tasks.
Storage options on the Jupiter motherboard are equally versatile, featuring an M.2 2280 slot supporting PCIe 2.0 x2, an eMMC connector, and a micro-SD card reader. These storage solutions ensure that the motherboard can adapt to different use cases, from fast boot drives to extended bulk storage. Furthermore, the Jupiter motherboard includes a PCIe x8 slot, albeit with PCIe 2.0 support, which might restrict it to older GPU models. Despite this, it offers ample expansion possibilities for other peripherals. The board’s connectivity features are comprehensive, including various USB ports (both Type-A and Type-C), an HDMI output capable of 1920×1440 resolution at 60Hz, Ethernet ports, and standard 3.5mm audio jacks. These attributes collectively emphasize the practical utility and versatility of the Jupiter motherboard across a wide range of applications.
Market Focus and Strategic Positioning
Milk-V’s strategic targeting of the Chinese consumer market with its Jupiter motherboard is an astute move that aligns with current trends and national policies. China has exhibited a growing interest in adopting RISC-V technology, strongly motivated by policies that advocate for technology localization and reduce dependency on foreign intellectual property. This positions the Jupiter motherboard favorably for adoption within China, where there’s an increasing push toward homegrown tech solutions. Beyond business strategy, this move is timely, given the geopolitical landscape that underscores the risks of over-reliance on foreign technology.
By offering the Jupiter motherboard, Milk-V taps into this burgeoning demand for localized technology solutions, presenting RISC-V as a viable and potentially superior option for various computing needs. This could potentially set a precedent for more widespread adoption of RISC-V technology, not just in China but also in other markets reconsidering their technological dependencies. Additionally, the emphasis on the Chinese market allows Milk-V to leverage local support and incentives aimed at fostering technological innovation. As Chinese companies and research institutions continue to collaborate on RISC-V projects, a robust ecosystem is emerging that can drive further advancements and applications of the open-source architecture. Thus, Milk-V’s Jupiter motherboard serves not only as a product but also as a catalyst for broader technological developments within China and potentially beyond its borders.
Comparative Analysis and Potential Challenges
In the world of consumer hardware, x86 and ARM architectures have typically monopolized the market, but Milk-V is disrupting the status quo with its new Jupiter mini-ITX motherboard, marking a significant leap for RISC-V architecture. The Jupiter motherboard represents not just a technological advance but also a strategic initiative aimed at capturing the expanding Chinese market. With its competitive specs and compact design, this product is set to change the way people view and use RISC-V technology, which has historically been more of an academic interest rather than a commercial player.
RISC-V is an open-source hardware instruction set architecture (ISA) celebrated for its potential to democratize cutting-edge computing technology. Historically, RISC-V adoption was confined to niche uses and academic experiments. However, recent geopolitical shifts and desires for technological sovereignty, especially in China, have reignited interest and investment in RISC-V. Milk-V’s Jupiter motherboard is a crucial milestone in moving RISC-V toward mainstream consumer use. Unlike proprietary x86 and ARM architectures, RISC-V offers more customization and potentially lower costs due to its open-source nature. Milk-V intends to exploit these advantages to meet China’s growing demand for indigenous technology solutions, making the Jupiter motherboard more than just a new product; it symbolizes a broader movement toward embracing open-source hardware.