Tucked away within your smartphone’s settings is a feature most people have never heard of, yet national cybersecurity agencies are now issuing urgent warnings about its potential to create a backdoor for hackers. This seemingly innocuous setting, a relic of a bygone era in mobile communication, has been identified as a significant and growing threat that requires immediate attention from both iPhone and Android users. The focus of this research summary is to explore what this threat is, why it is so dangerous, and what simple steps can be taken to secure your device.
Unveiling the Hidden Threat in Your Messaging App
The central theme of recent cybersecurity advisories revolves around a little-known smartphone function: the automatic downloading of Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) messages. This feature, enabled by default on most devices, allows your phone to receive and process multimedia content like images and videos without any interaction from you. While convenient in theory, this process creates a “zero-click” vulnerability, where malicious code embedded in an MMS message can be executed simply upon receipt, potentially compromising your device before you even see the message.
This is not a hypothetical scenario but an active threat that has prompted warnings from national cyber defense agencies. They are urging the public to take immediate action, highlighting the seriousness of the risk. The core of the danger lies in the silent, automated nature of the process, which bypasses the user’s critical judgment and hands control to potential attackers. Consequently, understanding and addressing this setting is no longer a matter of optional tech maintenance but a crucial step in personal digital security.
The Legacy Problem: Why an Outdated Technology Puts You at Risk
Multimedia Messaging Service is an archaic technology, first introduced over two decades ago as an upgrade to the text-only Short Message Service (SMS). It was designed to let users send photos, sound clips, and videos in an era before the widespread adoption of the internet and modern messaging platforms. Despite its age, MMS persists on modern smartphones primarily for backward compatibility, serving as a fallback for communication when data-driven apps like WhatsApp, iMessage, or Signal are unavailable.
The relevance of this outdated protocol to modern security was recently underscored by official warnings from national cyber defense agencies, including France’s ANSSI. These advisories have elevated a long-overlooked technical detail into a pressing concern for the average smartphone user. The fact that a 20-year-old technology can pose a risk to the latest iPhone and Android devices highlights a persistent challenge in the tech world: legacy systems often harbor security flaws that are later rediscovered and exploited by malicious actors.
Research Methodology, Findings, and Implications
Methodology
The analysis presented here is a synthesis of information drawn from multiple authoritative sources to provide a comprehensive view of the MMS threat. The research methodology involved a careful review of official cybersecurity advisories issued by government agencies responsible for national digital defense. This foundational guidance provides the official context and urgency for the issue.
Furthermore, this summary incorporates industry data and threat intelligence reports from leading cybersecurity firms, such as Proofpoint, which offer quantitative evidence of the rising threat landscape. To round out the analysis, expert commentary from respected technology journalists was reviewed to understand the practical implications for consumers and the broader industry context, ensuring the findings are both credible and accessible.
Findings
The primary finding from this research is that the automatic downloading of MMS messages creates a significant and exploitable backdoor for hackers. This default behavior allows a device to process incoming multimedia files without user consent, opening the door for zero-click exploits where malware can be delivered and executed silently. This vulnerability turns a basic communication tool into a potential gateway for device compromise.
This threat is not just theoretical; data shows it is a rapidly growing attack vector. A report from Proofpoint revealed a staggering 429% increase in unwanted MMS messages over a recent period. Attackers are increasingly favoring MMS for scams because multimedia content—using enticing images and graphics—is more effective at tricking users into providing confidential information or clicking malicious links compared to simple, text-based phishing attempts.
Implications
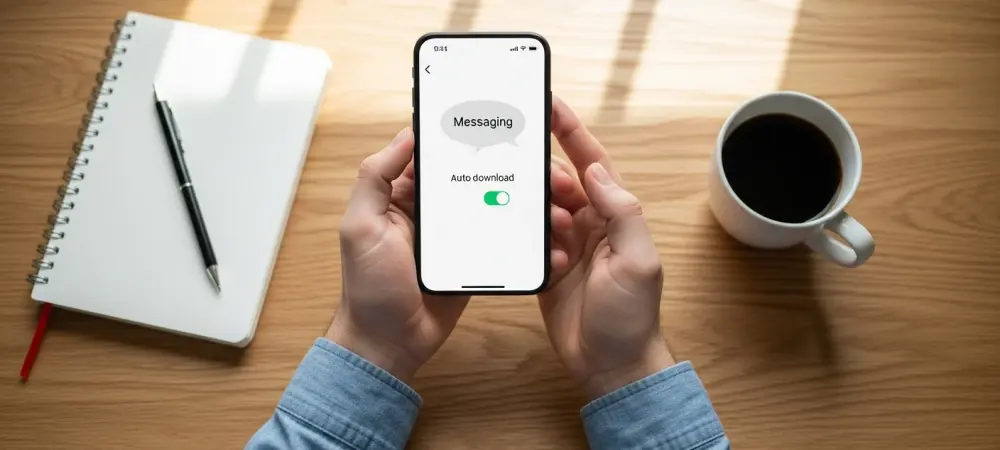
The practical implications of these findings are direct and actionable for all smartphone users. To mitigate this risk, it is strongly recommended to disable the automatic downloading of MMS messages. On an iPhone, this can be done by navigating to Settings, selecting Messages, and turning off the “MMS Messaging” toggle. For Android users, the path is typically found within the default messaging app’s settings, such as Google Messages, by tapping your profile, then Message Settings, followed by Advanced, and disabling any “Auto-download MMS” toggles.
Disabling this feature has a minimal impact on the modern user experience. Messaging through data-driven apps like WhatsApp, Telegram, or iMessage remains completely unaffected. However, users who frequently rely on traditional texting for group chats or sending media may notice a change. Instead of appearing automatically, incoming multimedia messages will require a manual tap to download, giving the user control over what content is processed by their device.
Reflection and Future Directions
Reflection
The re-emergence of MMS as a significant attack vector raises important questions about why such an old technology is becoming a burgeoning threat today. As security measures on modern operating systems and applications have become more robust, attackers are shifting their focus to weaker, often-overlooked legacy protocols that persist in modern devices. These older systems were not designed with today’s sophisticated threat landscape in mind, creating unforeseen security gaps.
A significant contributing factor is the low level of user awareness. Most smartphone owners are unfamiliar with MMS and its underlying mechanics, leaving the default, insecure settings unchanged. This highlights a broader challenge in cybersecurity: the persistence of outdated protocols in new technology and the difficulty of educating the public about hidden risks that may seem trivial but can have serious consequences for their digital safety.
Future Directions
Looking ahead, the discovery of this vulnerability should prompt action from device manufacturers and mobile carriers. A key question is whether these industry players will move to disable automatic MMS downloading by default in future software updates, thereby shifting the security posture to be safe by default rather than placing the onus on the user. Such a move would represent a significant step toward mitigating this threat at scale.
Further research should continue to monitor the evolution of MMS-based threats and analyze their effectiveness. Ultimately, the industry must accelerate the transition away from legacy messaging standards like SMS and MMS. Promoting wider adoption of secure, end-to-end encrypted protocols, such as the Rich Communication Services (RCS) standard, is essential for building a more resilient and secure mobile communication ecosystem for everyone.
Your Final Takeaway: A Simple Step for a Safer Phone
The research and expert warnings presented a clear conclusion: MMS represented an outdated and insecure protocol that exposed smartphone users to unnecessary risk. The automatic download function, enabled by default, was identified as a critical vulnerability that could be exploited by malicious actors without any user interaction.
Consequently, disabling this feature was recommended as a simple, direct, and highly effective security measure. This small configuration change was highlighted by cybersecurity experts as a crucial action in protecting personal data. It served as a potent reminder that in an era of increasingly sophisticated mobile threats, maintaining proactive digital hygiene and questioning default settings were essential for personal security.