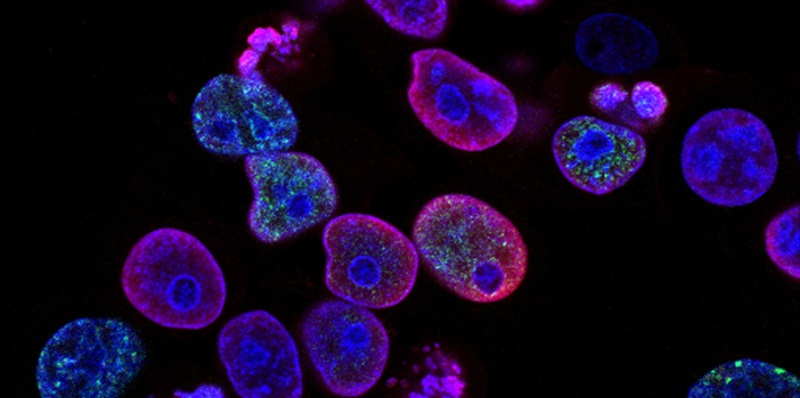
In the field of healthcare, the advent of artificial intelligence (AI) has brought forth numerous advancements. Among them is the groundbreaking technology called iStar. Developed to assist in the diagnosis and treatment of tumors, iStar utilizes AI algorithms to read medical images with exceptional clarity. With its ability to identify cancer cells that would otherwise be nearly invisible to doctors and scientists, iStar is poised to transform the way we approach tumor analysis and patient care.
Enhanced Detection of Cancer Cells
One of the most remarkable features of iStar is its ability to enhance the detection of cancer cells. By utilizing advanced AI algorithms, this innovative technology can provide unparalleled clarity when reading medical images. Through its precise analysis, iStar has the capability to identify cancer cells that would have otherwise gone unnoticed. This breakthrough has the potential to drastically improve early detection rates and ensure timely and accurate treatment.
Comprehensive understanding of gene function
In addition to its enhanced cancer cell detection capabilities, iStar also provides a comprehensive understanding of gene function within the context of tumor analysis. By automatically annotating microscopic images, iStar enables researchers and healthcare professionals to gain valuable insights into gene expressions and the intricate details of tumor biology. Moreover, iStar can assess whether safe margins have been reached during cancer procedures, thus enabling more precise surgical interventions.
Identification of tertiary lymphoid structures
iStar’s advanced AI technology goes beyond the analysis of cancer cells. It can also identify vital immune formations known as “tertiary lymphoid structures.” These structures have been found to be linked to a patient’s survival and response to immunotherapy. By accurately pinpointing and analyzing these formations, iStar equips medical professionals with a powerful tool for predicting patient outcomes, tailoring treatment plans, and developing targeted immunotherapies.
Training and methodology
To achieve its remarkable capabilities, iStar was trained using typical tissue pictures and leveraged the power of a machine learning tool called Hierarchical Vision Transformer. This training process equips iStar with the knowledge to capture the overarching tissue structures and focus on the minutiae in a tissue image, replicating the observations and expertise of a pathologist studying a tissue sample. This integration of machine learning algorithms and pathological knowledge enables iStar to analyze medical images with remarkable accuracy.
Mimicking a pathologist’s analysis
A significant strength of iStar lies in its ability to mimic the analysis performed by pathologists. With its focus on tissue structures and microscopic details, iStar replicates the observations and deductions made by experienced pathologists during the examination of tissue samples. By emulating this human-like analysis, iStar not only enhances accuracy but also expedites the diagnostic process, allowing for faster decision-making and more timely treatments.
Successful testing on various cancer tissue types
iStar’s potential has been demonstrated through successful testing on various cancer tissue types, including breast, prostate, kidney, and colorectal tumors. In each instance, iStar showcased its ability to identify and analyze cancer cells and their associated features with remarkable precision and accuracy. These promising results underline the versatility and potential impact of iStar in diagnosing and treating a wide range of tumors.
Superior speed compared to competing tools
Beyond its accuracy and reliability, iStar showcases superior computational speed compared to other similar AI tools. While rival tools may take hours, iStar’s advanced algorithms complete its analysis in under nine minutes. This significant reduction in analysis time empowers healthcare professionals to conduct large-scale biomedical studies efficiently and paves the way for extended applications in 3D imaging and biobank sample prediction.
Potential for Large-Scale Biomedical Studies
The unmatched speed of iStar opens doors for large-scale biomedical studies and research. With its ability to analyze vast amounts of data in a fraction of the time, researchers can now explore extensive datasets to gain deeper insights into tumor biology, patient outcomes, and therapeutic strategies. Additionally, iStar’s rapid analysis enables timely decision-making, potentially accelerating the development of personalized medicine and more targeted treatments.
Future developments and applications
As with any groundbreaking technology, the potential for iStar’s future developments is both exciting and promising. Researchers hope to further enhance its understanding of tissue microenvironments, providing clinicians with invaluable knowledge to improve diagnosis and therapy. By continuously refining iStar’s algorithms and integrating it into clinical practice, we can expect to witness ongoing advancements that revolutionize tumor analysis, treatment approaches, and, ultimately, patient outcomes.
The emergence of iStar represents a transformative milestone in tumor diagnosis and treatment. With its unparalleled ability to identify nearly invisible cancer cells, provide comprehensive insights into gene function, and analyze immune formations linked to patient survival, iStar equips healthcare professionals with a powerful toolset. Furthermore, its superior speed compared to competing tools opens doors for large-scale biomedical studies and accelerates progress in personalized medicine. As iStar continues to evolve, we can expect even greater breakthroughs in our understanding and management of tumors, revolutionizing patient care for years to come.